orbital.algorithm.template
Interface TransitionModel
- Type Parameters:
A - the type of transition actions.S - the type of transition states.M - the class representing transitions.
- All Known Subinterfaces:
- GeneralSearchProblem, MarkovDecisionProblem
- All Known Implementing Classes:
- DelegateGeneralSearchProblem, OpenClosedGeneralSearchProblem
public interface TransitionModel
Represents a transition model.
The central part underlying several other formalizations of systems
consists of such a transition model.
A transition model is a mathematical model for (formal) systems with states
and action-driven state changes.
It forms a rewrite system, perhaps with additional probability information.
A transition model is characterized by
- a state space set S.
- a set of actions A.
- sets of actions A(s)⊆A applicable in each state s∈S.
Usually A(s)
= {a∈A ¦ ∃sʹ∈S∖{⊥} P(sʹ|s,a)>0}
= {a∈A ¦ τ(a)(s,⊥)≠1}
= A∖τ-1({s}×{⊥})
= τ(a)(s,·)
= (τ(a)(s,·))-1((0,1])
-
the action-dependent (stochastic) transition relation
τ:A→(S×S→[0,1])
on S specified as either
-
deterministic transition function t:S×A(s)→S,
with t(s,a) being the next state reached (for sure) when performing action a∈A(s) in state s∈S.
τ(a)(s,sʹ) := 1 iff sʹ=t(s,a)
-
non-deterministic transition function t:S×A(s)→℘(S),
such that t(s,a) is the set of next states that could be reached when performing action a∈A(s) in state s∈S.
τ(a)(s,sʹ) := 1 ⁄ |t(s,a)| iff sʹ∈t(s,a)
-
non-deterministic transition relation T⊆S×A(s)×S,
such that ⟨s,a,sʹ⟩∈T iff sʹ is a next state that could be reached when performing action a∈A(s) in state s∈S.
τ(a)(s,sʹ) := 1 ⁄ |{sʹ∈S ¦ T(s,a,sʹ)}| iff T(s,a,sʹ)
-
stochastic transition probabilities Pa:S→[0,1]; sʹ↦Pa(sʹ|s) := P(sʹ|s,a) := P(St+1=sʹ|St=s,At=a)
denoting the probability of reaching state sʹ∈S on taking the action a∈A(s) in state s∈S.
The function P is written this way in order to remind that it has a specific probability distribution.
Another possibility would be to use a combined function
t:S×A(s)→℘(S×[0,1]); (s,a)↦{⟨sʹ,P(sʹ|s,a)⟩ ¦ sʹ∈S}
which is more closely related to implementation issues (and thus used here),
but usually considered inconvenient for the pure purpose of notation.
Stochastic transitions provide the most general case of these types of transitions.
τ(a)(s,sʹ) := P(sʹ|s,a)
As a notation for a transition from s∈S to sʹ∈S under the
action a∈A(s) with transition probability p∈[0,1] we sometimes use
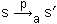
here.
τ(a⋅b) = τ(b)∘τ(a) = ((s,sʹ) ↦ P(⋁z∈S(St+2=sʹ∧St+1=z) | At+1=b,St=s,At=a))
= ((s,sʹ) ↦ ∑z∈S τ(a)(s,z)*τ(b)(z,sʹ))
The last equation is true if the events are independent, f.ex. for a transition model
satisfying the Markov property
for states.
In the same manner, τ(an) = τ(a)n is the
(stochastic) transition relation for n transitions of fixed action a∈A.
τ(a*) = τ(a)∞ is the transitive closure with a fixed action.
A non-deterministic transition model is a semi-Thue system with CH3 acception rules
(more precise: reductions).
Note that you can as well use this interface in its raw version (i.e. without instantiating
template parameters) for mere non-deterministic transitions without stochastic information
by ignoring the type-restriction of TransitionModel.Transition to transition(Object,Object,Object).
- Author:
- André Platzer
- See Also:
TransitionPath,
Function,
BinaryPredicate
|
Nested Class Summary |
static interface |
TransitionModel.Transition
Represents (information about) a transition option during a transition model. |
|
Method Summary |
java.util.Iterator |
actions(java.lang.Object state)
Get the applicable actions at a state. |
java.util.Iterator |
states(java.lang.Object action,
java.lang.Object state)
Get all states reachable with any transitions from the state under a given action. |
TransitionModel.Transition |
transition(java.lang.Object action,
java.lang.Object state,
java.lang.Object statep)
Get (information about) the transition from a state to another state under a given action. |
actions
java.util.Iterator actions(java.lang.Object state)
- Get the applicable actions at a state.
Intuitively, applicable actions are those that result in a valid
transition. So for a state, the applicable actions are the only
actions relevant for leaving that state with any transition
(including transitions that lead back to the state the
transition just started in).
For several reasons (including performance) it is widely recommended that
A(s) = {a∈A ¦ ∃sʹ∈S∖{⊥} P(sʹ|s,a)>0}
= {a∈A ¦ τ(a)(s,⊥)≠1}
= A∖τ-1({s}×{⊥})
= τ(a)(s,·)
= (τ(a)(s,·))-1((0,1])
In fact, this is not a strict requirement, if the computation would be far too
expensive. However, the TransitionModel implementation would then have to deal with
cases where an action was chosen that has later been found out to be inapplicable,
contrary to the initial guess of actions(Object).
Since this may result in rather messy implementations, relieving this requirement
should generally be limited to very specific and well documented cases.
- Parameters:
state - the state s∈S whose applicable actions to determine.
- Returns:
- A(s)⊆A, a list of alternative actions applicable in the state s∈S.
The order of the list can be decisive because for actions with equal costs
the first will be preferred.
- See Also:
GreedyProblem.nextCandidates(java.util.List)- Preconditions:
- s∈S
- Postconditions:
- RES=A(s)⊆A
states
java.util.Iterator states(java.lang.Object action,
java.lang.Object state)
- Get all states reachable with any transitions from the state under a given action.
Intuitively, those are the only relevant states which can be reached
by any transitions (from the given state under the given action) at all.
For performance reasons it is recommended that this method does only return
those states sʹ∈S that can truely be reached
(i.e. where P(sʹ|s,a) > 0, i.e.
sʹ ∈ {s}∘τ(a) = {sʹ∈S ¦ τ(a)(s,sʹ)>0}).
Although this is not strictly required if it would be too expensive to determine.
Note that the resulting iterator will never be empty since the
transition probabilities sum up 1 (or integrate to 1 in the
case of a continuous transition probability distribution),
even though the next state may not differ from the previous
state.
- Parameters:
action - the action a∈A(s) that must be applicable in state s∈S.state - the state s∈S.
- Returns:
- a list of states sʹ∈S that could be reached
when performing the action a in the state s.
- Throws:
InapplicableActionException - if a∉A(s) is not applicable in state s.- Preconditions:
- s∈S ∧ a∈A(s)
- Postconditions:
- RES ⊇ {s}∘τ(a) ∧ RES.hasNext()
transition
TransitionModel.Transition transition(java.lang.Object action,
java.lang.Object state,
java.lang.Object statep)
- Get (information about) the transition from a state to another state under a given action.
This central method specifies the central action-dependent (stochastic) transition relation
τ:A→(S×S→[0,1])
on S. With transitions specified by τ(a)(s,sʹ)
In usual cases, implementations can assume that action stems from some call to actions(Object),
and statep is obtained from states(Object,Object).
- Parameters:
action - the action a∈A(s) that must be applicable in state s∈S.state - the source state s∈S prior to the transition.statep - the resulting state sʹ∈S after the transition took place.
- Returns:
- τ(a)(s,sʹ) which is the probability P(sʹ|s,a)
of reaching state sʹ∈S when performing action a∈A(s) in the state s∈S.
Usually represented as a
transition
which may contain additional information.
- Throws:
InapplicableActionException - if a∉A(s) is not applicable in state s.- Preconditions:
- s,sʹ∈S ∧ a∈A(s)
- Postconditions:
- RES=τ(a)(s,sʹ)∈[0,1] (more precisely RES.getProbability()=τ(a)(s,sʹ)) ∧ ∑sʹ∈S τ(a)(s,sʹ) = 1
Copyright © 1996-2009 André Platzer
All Rights Reserved.